The user is the person who uses the internet and is normally looking for information. These people normally look through the internet without knowing much about it. The user can be entertained and informed through the internet through apps and programs. If there is no user the computer is just a hollow piece of metal probably only useful as a paper weight.

A browser is a program with an interface for displaying HTML files on the world wide web. Firefox, chrome, safari, internet explorer and opera are all browsers that people use every day of there lives which help them gather information from websites.

A device is a machine that is used by the user. The device can not do anything unless someone is using it or if they are programmed to do stuff. PC, phones and tablets are all devices that the user uses normally everyday of there life in heaps of countries.

An Internet service provider (ISP) is an organization that provides services accessing and using the Internet. Internet service providers may be organized in various forms, such as commercial, community-owned, non-profit, or otherwise privately owned.

A webpage is a hypertext document connected to the world wide web. Web pages can be either static or dynamic. Static staying the same every time you go on that page while dynamic pages have content that can be changed each time.
The World Wide Web or www for short is an information space where documents and other resources are identified by URl or Uniform Resource Locators and can be accesed via the internet.

a combined device for modulation and demodulation, for example, between the digital data of a computer and the analogue signal of a telephone line.

A computer network or data network is a telecommunications network which allows nodes to share resources. In computer networks, networked computing devices exchange data with each other using a data link. The connections between nodes are established using either cable media or wireless media.

A Web server is a program that uses HTTP Hypertext Transfer Protocol to serve the files that form Web pages to users, in response to their requests, which are forwarded by their computers' HTTP clients. Dedicated computers and appliances may be referred to as Web servers as well.
A cable consisting of one or more thin flexible fibres with a glass core through which light signals can be sent with very little loss of strength.

Web hosting is a service that allows organizations and individuals to post a website or web page onto the Internet. A web host, or web hosting service provider, is a business that provides the technologies and services needed for the website or webpage to be viewed in the Internet. Websites are hosted, or stored, on special computers called servers.

Packets are the small pieces of data that is one whole piece of information just split up into smaller bits so they can be transported more swiftly to its next location. If a package goes missing e.g if there were 6 packages all named through numbers 1-6 and number 5 went astray the computer would send back a reply sayng that it hasn't made it there. The first computer would resend package five until it gets through.
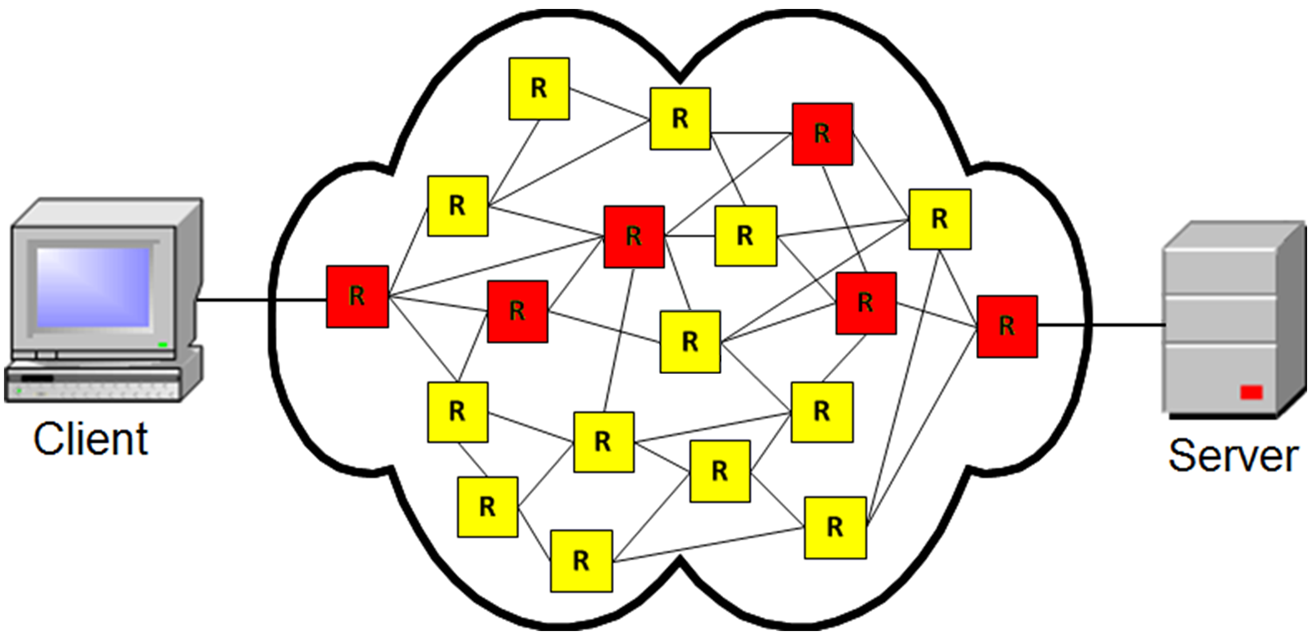
A router s a networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks. Routers perform the traffic directing functions on the Internet. A data packet is typically forwarded from one router to another router through the networks that constitute the internetwork until it reaches its destination node.

LAN or Local Area Network is a network that stays in a small remote area. RAN or Regional Area Network which stays within the region and both of these connect to WAN or World Area Network.
URL stands for Uniform Resource Location is a reference to web resorces that specifies its location on a computer network and a mechanism for retrieving it. This is the Url to this website.
URLs (Uniform Resource Locators) and IP addresses are just identifiers used for this purpose. The main difference between URL and IP address is what they point to. ... In comparison, a typical URL contains the protocol to be used (i.e. HTTP, FTP), the domain name or IP address, the path, and optional fragment